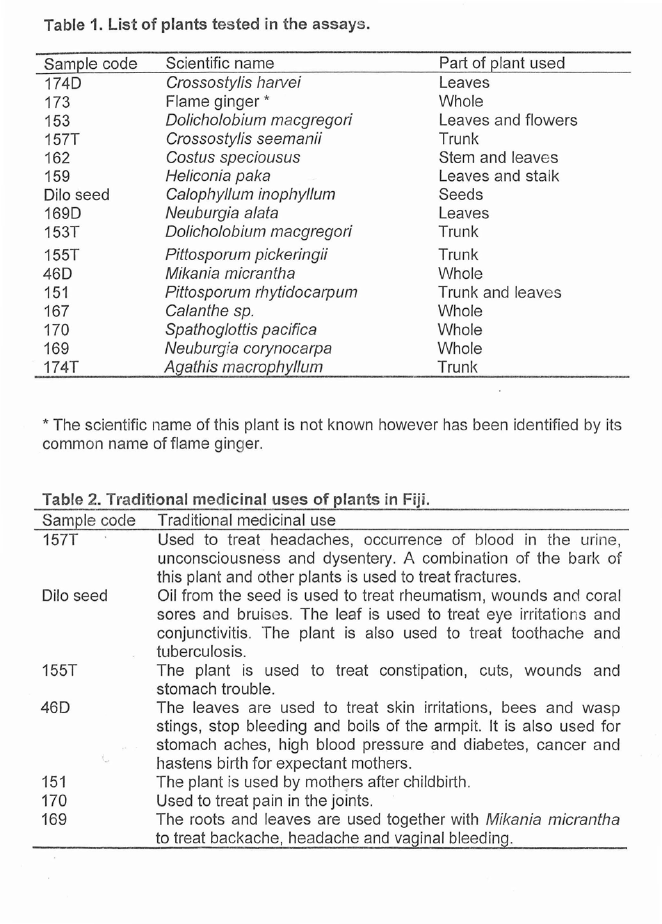
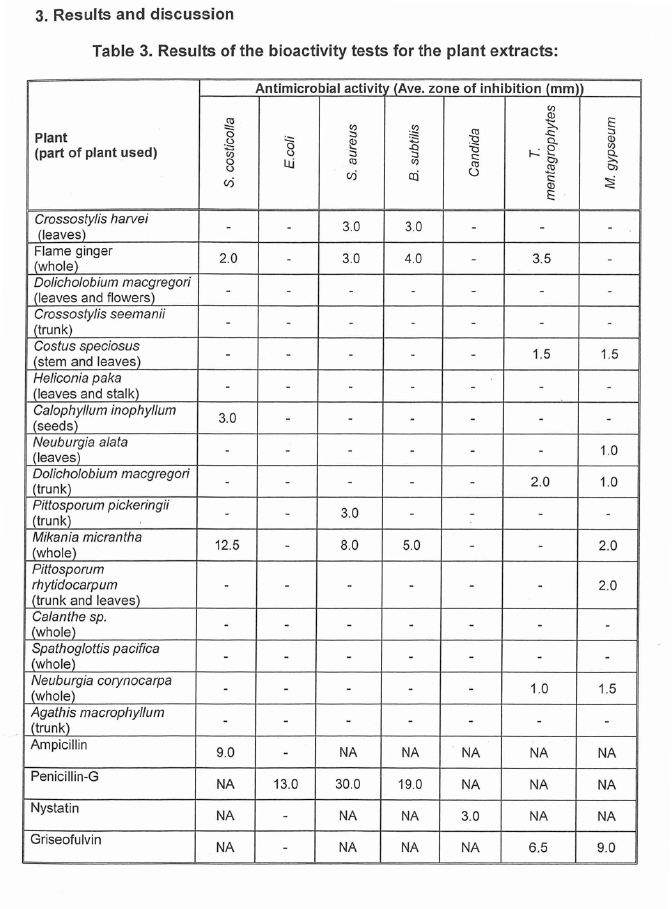
opportunistic pathogen causing food poisoning. The three fungi include the yeast
Candida albicans and two moulds Trychophyton mentagrophytes and
Microsporum gypseum. C. albicans causes infections of the mucosa! membranes
of the body known as candidiasis. T. mentagrophytes (var. mentagrophytesi) and
M. gypseum are common human dermatophytes causing cutaneous mycoses
such as tinea pedis (atheletes fo ot), tinea corporis (ringworm of the smooth or
bare parts of the skin), tinea cruris (ringworm of the groin), and tinea unguium
(infection of the nail bed). Due to the pathogenic nature of these microoganisms
these tests were done in a biosafety cabinet (class II) using sterile techniques.
2. Methodology
1. Sample preparations:
All the samples were dried, ground and soaked in methanol overnight.
This extraction process was repeated twice. The combined methanol extracts
of the samples were then filtered and reduced under vacuum.
The dried crude extracts (100mg) were then dissolved in 80% dimethyl
sulfoxide (DMSO) in water to make concentrations of 250mg.mr1. The
dissolved samples (1 0~tl) were then transferred to sterile paper disks (6mm
diameter) and dried and then used in the assays.
2. Antibacterial assay:
This assay employed four bacteria, S. costicol/a, E. coli, B. subtilis and S.
aureus. Seed cultures (3ml) were prepared for each bacterium in the
following way. Nutrient broth (NB) was used to culture E. coli, B. subtilis and
S. aureus, however, marine broth (MB) was used for S. costicolla . The
prepared media (3ml) for each bacterium was autoclaved, cooled ;:md
inoculated with each bacterium using sterile 10µL loops and the culture"
incubated at 30°C overnight while shaking.
For the assay plates, nutrient agar (NA) was used to culture E. coli, B.
subtilis and S. aureus, however, marine agar (MA) was used for S. costicolla.
The media (50ml) for each bacterium was autoclaved and then cooled to
45°C and inoculated with overnight seed cultures. MA (50ml) was inoculated
with 1.5ml of overnight broth culture of S. costicol/a, while for the other test
bacteria, 50ml of NA was inoculated with 50µL of overnight broth culture. The
inoculated media were then poured into tissue culture plates, allowed to
solidify, and then used in the bioassay.
Prepared sample disks were then placed on the assay plates together with
a known standard for that particular bacterium used as a positive control. The
plates were incubated as follows. E. coli and B. subtilis plates were incubated
at 37°C while S. aureus and S. costicol/a were incubated at 30°C. The results